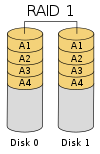
Advantage of this method: Even if one disk fails, we can still read the whole data from the other disk where the data was stored, provided it is working fine. Thus our system can still stay up and running while the affected disk is being replaced!
Those who want to know more about the other ways of doing this, check this link out
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RAID#Standard_levels
Now we come to the advantages and disadvantages of using a RAID disk
Advantage:
1) They can make excellent backup drives especially when they are employed as backup devices to the main drives and particularly when they are located away from the main system.
2) It increases the performance and reliability of a system as regular checks are done to check for any possibility of a system crash
Disadvantage:
1) RAID disks are essentially designed and extensively written for servers. Thus if there is a server, there has to be a network as well and this can cause configuration issues as each network is different.
2) High cost of Purchase (doesn't cost less than a few thousand of dollars)
This post would be incomplete without any mention of WHEN do we use a RAID. It is all very well knowing what RAID does but not knowing when to apply it can be problematic in view of the high cost of purchase as mentioned above.
We can use them in mainly 3 ways:
1) Business Servers: Large business companies require a secure way of storing large amounts data without suffering any loss of the same. RAID can be used for this purpose especially if it is stored in a remote location where accidental erasure of data is pretty much impossible to do.
2) Workstations: "Individuals who are doing intensive work such as video file editing, graphical design,etc. should use a RAID" (taken from http://www.pcguide.com/ref/hdd/perf/raid/why.htm) RAID 0 will provide the improved performance needed in many of these applications (remember what I wrote earlier about improved bandwidth?).
3) Home PC: Most of us use this and we don't need RAID as the high cost of purchase is not justified by the activities we perform with the PC. It's better for us to use SATA/IDE instead (For those who don't know what SATA/IDE is, go here http://smblog.iiitd.com/2010/07/hard-disks-advantage-of-sata-over-ide.html).
Thus we can say that RAID is best used by big companies that can afford to purchase it as it gives them their money's worth over the security of their data which is a very important thing in this world.
If anyone wishes to add something else to the above, go ahead and do so =D
SOURCES:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RAID
http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/R/raid.html
http://www.ecs.umass.edu/ece/koren/architecture/Raid/raidhome.html
http://www.raid-data-recovery.net/advantages-raid.html
IMAGES:

very well explained that too in such simple language..really liked this post..thanku..
ReplyDeleteA really informative one. You are a very good writer Shayan.
ReplyDeleteThanks Udit and Soumyavardhan :D
ReplyDeletevery well written shayan. just a little question though. How the data is actually written on the magnetic disks?(Like in the case of cds and dvds its in the form of pits and lands)
ReplyDeleteTanmay-This is the best answer that i could find for your question without going into too much details
ReplyDeletehttp://wiki.answers.com/Q/How_is_data_initially_written_on_a_magnetic_disk
Unfortunately the link isn't working directly, so you'll have to copy and paste it to the address bar :\
Nicely written post!
ReplyDeleteYou explained it very well without using technical terms that we wouldn't understand :P
Are you going to inform us about the remaining RAID configurations anytime soon (RAID 2, RAID 3, RAID 4, RAID 5, RAID 6, Hybrid RAID, etc.)???
ReplyDeleteI'm looking forward to a follow up blog post.